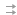102-112
An Investigation on Soil Quality and Heavy Metal Levels in Soil of Rajbandh Waste Disposal Site at Khulna, Bangladesh
Authors: K. Fahmida and I.M. Rafizul

Number of views: 326
The principle objective of this study was to evaluate the soil quality and the level of contamination of
soil by heavy metals adapting various developed index in a selected waste disposal site at
Rajbandh, Khulna, Bangladesh. To theses endeavor, ten soil samples were collected from the selected
locations and then the relevant elements of Al, Fe, Mn, Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn, Ni, Cd, As, Co, Sb, Sc and Hg
were measured and monitored using standard method. To estimate the contamination situation of soil,
contamination factor (CF), enrichment factor (EF) and geo-accumulation index (Igeo) and potential
ecological risk index (PERI) were computed using geological background values. In addition, for
assessing soil quality, Pearson's correlation coefficients analysis was also performed. Furthermore,
this study revealed that the values of CF and Igeo in soils around the waste disposal area affected from
the contamination of heavy metals mostly by Pb, Cd and Sb. In contrast, Pearson's correlation indicated
that the sources of metals are almost the same and these heavy metals might be derived from the waste
accumulation activity. Dump sites have great potential for energy extraction if the high valued
compounds to be extracted.
 Today
Today Yesterday
Yesterday This week
This week Last week
Last week This month
This month Last month
Last month All days
All days